Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Logging in using QR
Instead of asking a user for their username and password, you can let them log in to your website by showing them a QR code they need to scan. In this scenario, you will see how to implement this process.
How does it work?
The process for logging in passwordless, with a QR code can be seen below.
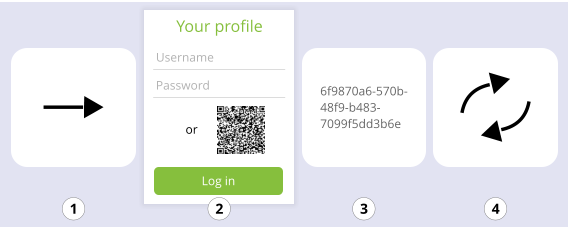
- You redirect the user to the login page.
- User chooses to login with QR.
- A screen with QR code along with a countdown bar is shown.
- User opens the mobile app and scans the QR code.
- User is logged in into the web application.
You know the user is logged in as soon as you reach step 5, but you need the access token to call other API endpoints.
What APIs do you need?
In order to achieve the flow described above, the authentication API is required, and the needed modules are QrCodeAuthentication and QrCodeScanRequired.
An example of an authentication request for issuing a QR code to authenticate the user with can be seen below:
curl --request POST \ --url https://www.onewelcome.com/onewelcome-dev/login/api/authenticate \ --header 'content-type: application/json' \ --data '{ "module": "QrCodeAuthentication", "definition": { } }'The response of this API contains the QR code, along with an attribute which specifies for how long the QR code is valid.
{ "nextModule": "QrCodeScanRequired", "additionalInformation": { "validityPeriod": 120, "qrCode": "iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAAfQAAAH0AQMAAADxGE3JAAAABlBMVEX///8AAABVwtN+AAACY0lEQVR42uzcQY6jMBCF4UJZZMkRcpQcLRyNo+QILFmgrhG2y2XTMEMY1FKL/61mGj52JTvlAiGEEEIIIYQQ8pvSqGeUh4Y/vsJ/v6TVvtFRRIqbJjwe736wf0Z/i7cN8dHmR7vphcfjT/XPGfRilfouL335o8MlPB6/5UP9hZvaef2T+dKIx+N/xIc8tBNptWviIojH4//mff9o699Nh/lHnG0id+8/8Xj8Z37RP8nrX5f2n/fZ7++/4PEX8nWs/zjlJqR66e0IHo//xKf95xg3oe9cqYO8Yusk1m9YGqd5Ezrh8fhy/evjJlHuqvX5mdj65/XZCR6PP8uLtLbIaZmheLRqeHRxNIDH4xf9R6s/K7ImFuE9XgpdEd1aP/F4/EEfmvzPPH8VNpnp/KzK7DvB4/Hf+o+pyMKPNDs/S/2PZ9GaFDwef5oXG/JI/ROfX3ylp3pr8rZyfo3HX9u3cZMYfqSF+kt/7YqjtXhJV9Y/PB5/3OchYa9fn1/MQ4zemhQ8Hl/Vn/XvJR6SlfXXi3l/NB6PP8nnISs7BJisUxLf35TF/NXG+ofHX9KLD3kU+8dvfox/fW+NUeHx+EO+taOzYsg+V6qVttr59er6icdf1tfzv9UiV24tw6naY2v9w+PxB/zy/RcbEvb3n/Or0auvvuDx1/b19290Kta/Ns9Pyb73n/F4/Ke++n7OVD2kLw/R1uf38Xh88f0b1e4Wpxrz0dre+sPj8f/l0532/mbjX/XA4/H/+P5NNX/vrcmw/m3O7+Px+IN+7fvbdf/ERq/weDwhhBBCCCGEkB/NnwAAAP//HGpqhRcoOygAAAAASUVORK5CYII=", "qrCodeTrackId": "0bf51e27-7251-4b74-82bc-40a33386fe2f", "nonce": "046dd280-0d00-4a3d-87de-d031915afdcd" }}| Attribute Name | Attribute Description | |
|---|---|---|
| nextModule | Specifies the next module to be used in order to continue with the authentication process. If next module is Success, it means that you are authenticated. | |
| additionalInformation.validityPeriod | Indicates for how long the QR code is valid. The returned value is in seconds, and if the user scans the QR code after validityPeriod, the request will fail. | |
| additionalInformation.qrCode | Represents the base64 encoded value of the QR code. | |
| additionalInformation.qrCodeTrackId | Random value generated by the backend server, which needs to be sent in subsequent authentication requests, either as a cookie or in the payload. | |
| additionalInformation.nonce | Represents a random value, which has to be sent in subsequent authentication requests for verifying if the scanning of the QR has been performed. |
Once you have a QR code, you can show that to the user, along with a timer filled with the value from the response.
Now that the QR code is available to the end-user, you have to send regular requests to verify if the user scanned the QR code. In order to do so, you have to call the API described below:
curl --request POST \ --url https://www.onewelcome.com/onewelcome-dev/login/api/authenticate \ --header 'content-type: application/json' \ --data '{ "module": "QrCodeScanRequired", "definition": { "nonce":"327aab40-89d3-456d-87f8-8943085fafdd", "qrCodeTrackId":"e5e66b49-a367-4f9e-b83f-9a6c8460443e" }}'Using the data returned from the previous API, this API can be called regularly, to verify if the user managed to scan the QR code. We recommend calling this API at fixed time intervals, from two to three seconds, in order to not overload the server with unnecessary requests, since it is less probable that the user will be able to open the app and scan the QR code in within a second. If the user did not manage to scan the QR code in time, the API will respond with a 400 bad request with following error response:
{ "code": 1020, "message": "Qr code expired because it hasn't been scanned in an interval of 120 seconds"}This is an error from which you cannot recover, but what you can do instead is to offer a possibility to the user to generate a new QR code. If the user successfully scans the QR code, the response from below will be returned:
{ "nextModule": "Success", "token": "AQIC5wM2LY4SfcyLh7kwYcsc78wgrESNaR_B2E6QOX_tHRU.*AAJTSQACMDIAAlNLABMyMTQwMzc4OTQ3NzE1NTYyMzU0AAJTMQACMDE.*", "jwtToken": "eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJleHAiOjE2MTgyNDEwNjEsImlhdCI6MTYxODIzOTMyMSwiaXNzIjoiaHR0cHM6Ly93d3cub25nby5jb20vYXV0aC9vYXV0aDIuMCIsInN1YiI6IjBmMDdhNTA2LWE2NDItNDg0Ny1iNTU5LTBiNmZmNzVjZWYyMSIsImF1ZCI6WyJpd2VsY29tZSIsIm9hdXRoMm9uZ28iXSwic2VnbWVudCI6Im9uZ28iLCJhdXRob3JpdGllcyI6WyJST0xFX3VzZXIiLCJST0xFX3VzZXJfb25nbyJdLCJncm91cHMiOlsidXNlcnMiLCJ1c2Vyc19vbmdvIl0sInVzZXJfbmFtZSI6IjBmMDdhNTA2LWE2NDItNDg0Ny1iNTU5LTBiNmZmNzVjZWYyMSJ9.dj2JlQNpfT8Z8cCMBdGquUUjpvpQp3-P_j8mNMlNnk0", "oauth2Token": "fab878f2-441b-4155-a050-bd969c3cb6f3", "userData": { "userName": "testAccount", "emailAddress": "testAccount@yopmail.com", "title": "mr" }, "settings": { "continueWithoutSecureLogin": true, "redirectUrl": "/your-app/profile" }}| Attribute Name | Attribute description | |
|---|---|---|
| nextModule | Specifies the next module to be used in order to continue with the authentication process. If next module is Success, it means that you are authenticated. | |
| token | Represents the single sign on token. | |
| jwtToken | A JWT token with details about the authenticated user. | |
| oauth2Token | Oauth2 access token, which can be used to access different APIs. | |
| userData | Depending on the authentication module used, at the end of the process, this attribute may contain different properties. | |
| settings | The object contains a set of configured properties, which helps calling applications to redirect the user to a configured page upon successful authentication. |