Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Access
Access to information is governed by a combination of roles & role types, system rules and flexible structures.
Roles
A role is a collection of permissions that control what data and applications a user or application can access and what actions he/she can perform. Roles are defined per segment. Therefore, you can assign different roles for different segments. Additionally, an identity can have multiple roles associated to it.
A role type determines the scope of the role and the available entitlements. Once it is selected for a specific role, it cannot be changed.
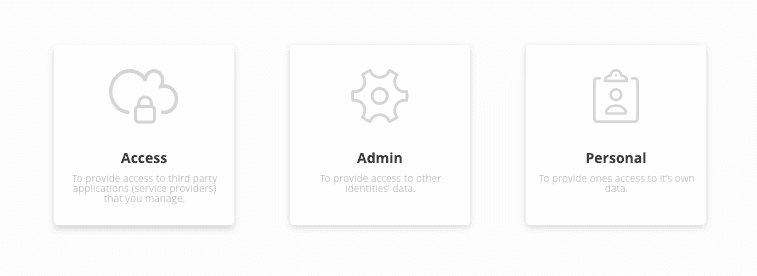
The applications make available the following types of roles:
- Access role
- Admin role
- Personal role
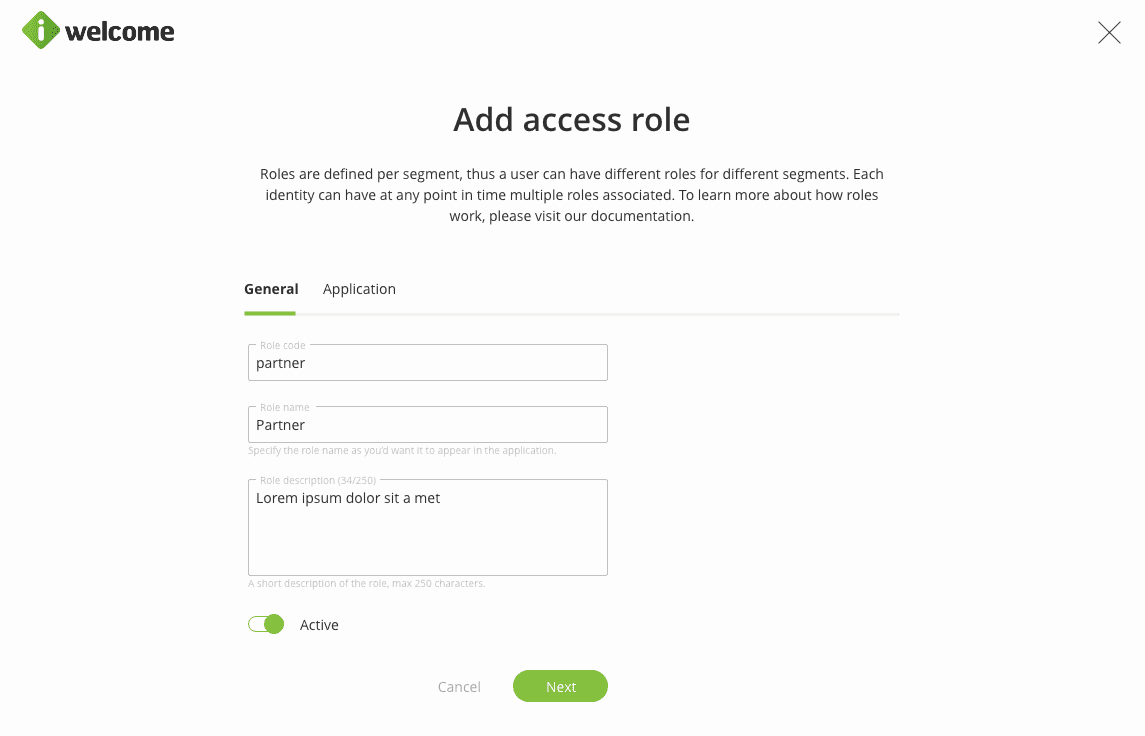
Access role
This provides access to applications for the users that have them associated. The same role might provide access to one or more applications. Also, during the single sign-on process, the platform passes to the application the application roles that were defined for it and that were selected while defining the role.
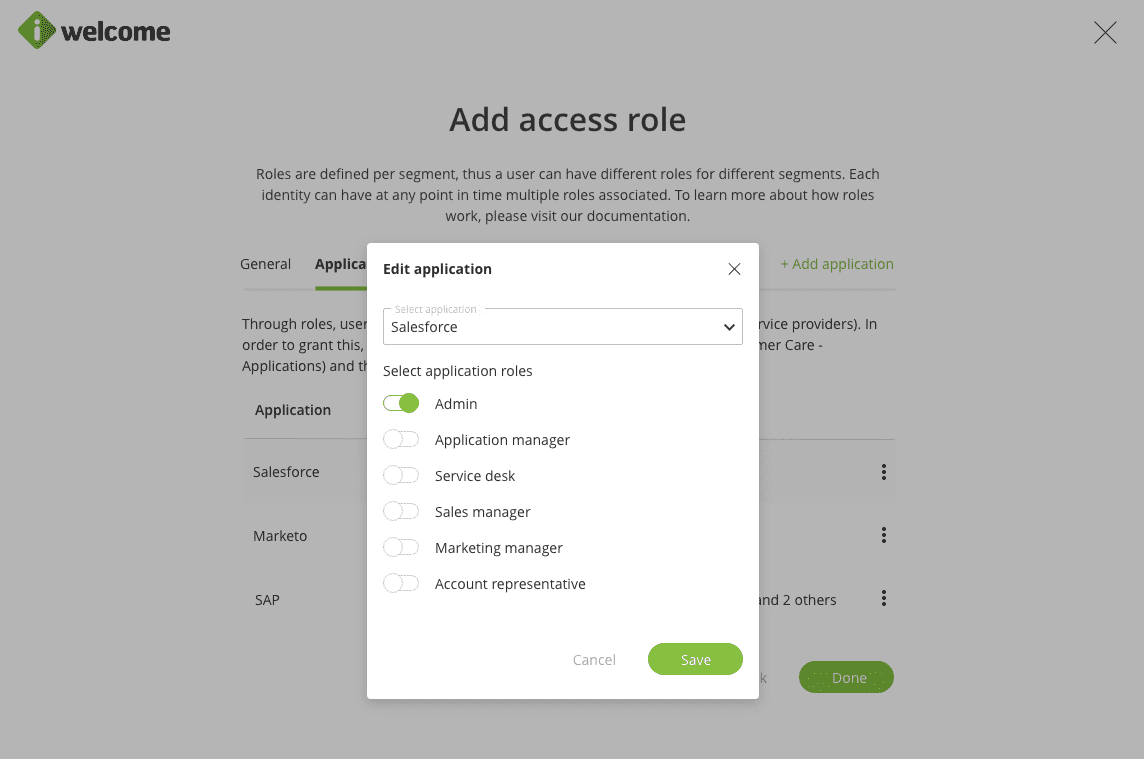
Before defining an access role, the service provider (application) has to be set up under Applications. The process will ask the admin user to select the application the role will grant access to and the list of application roles that will be passed through the access token when performing single sign-on.
Admin role
This provides users that have them associated access to the platform, and through it, to the other identities that are managed inside it. Access to other identities is controlled through entitlements that define the scopes (list of identities that a user with a specific role might affect) and actions that can be performed, including the option to delegate certain access rights to the identities in the scope.
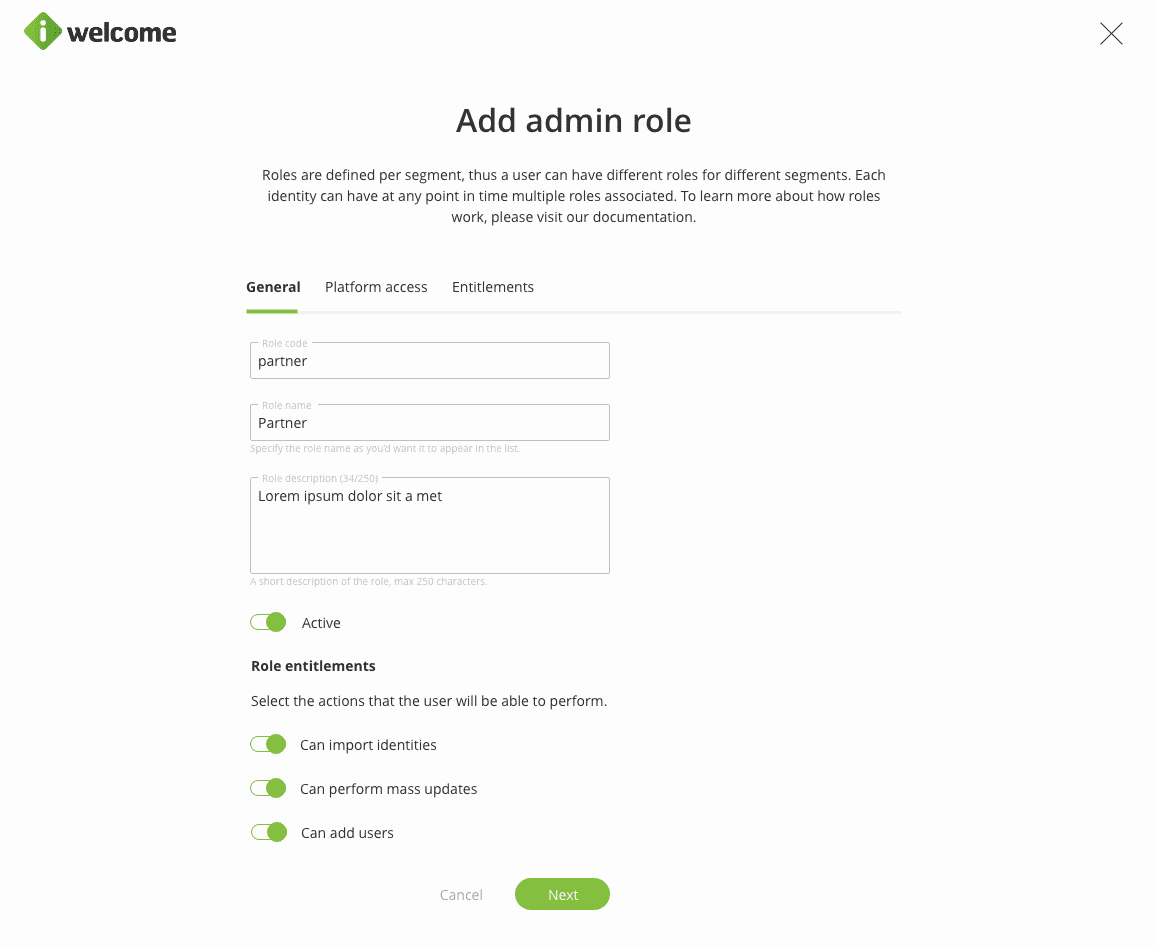
When adding or editing a role, besides the generic information, the admin user will also have to select the menu item that a user having the associated role is granted access to. The menu options can be edited later on and the effects are propagated right away.
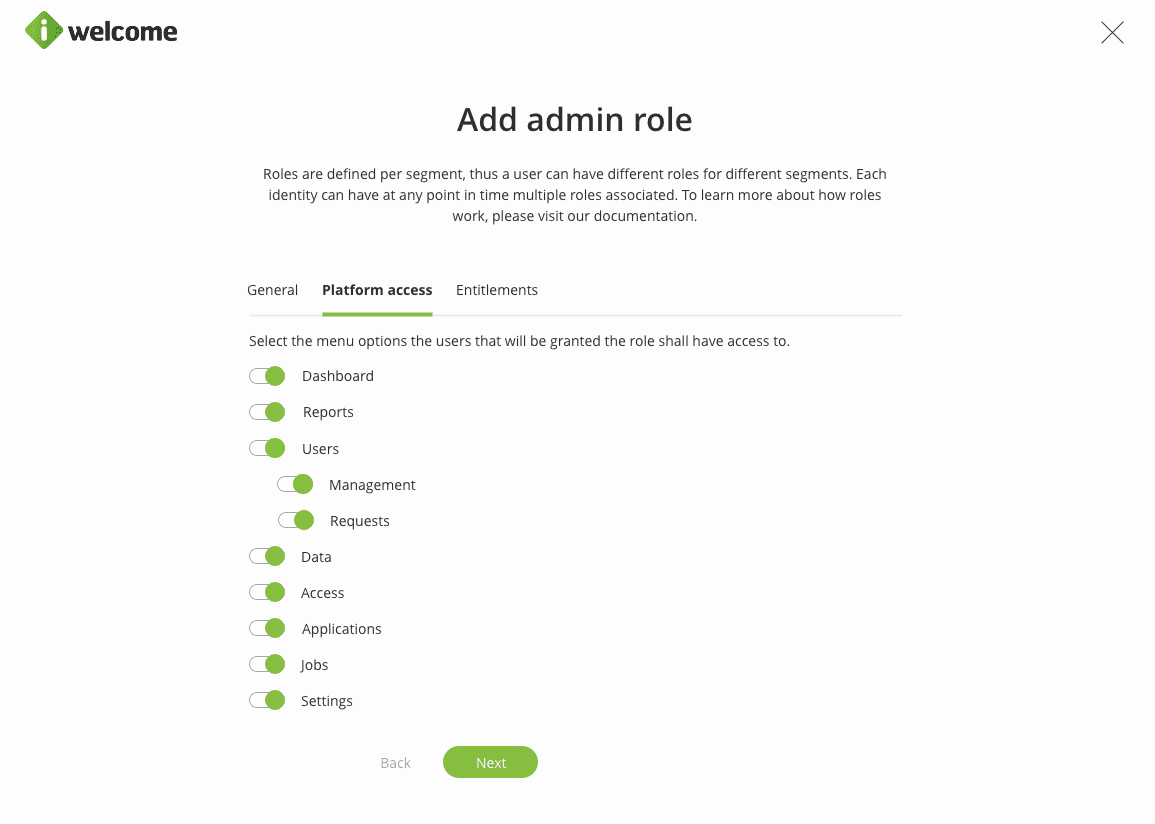
Users' access can be restricted further by defining the scope (the dynamic list of identities he/she can affect), the action he/she can perform on the selected identities, and the roles he/she can assign to the managed identities. This objective is achieved by defining one or more entitlements for each admin role.

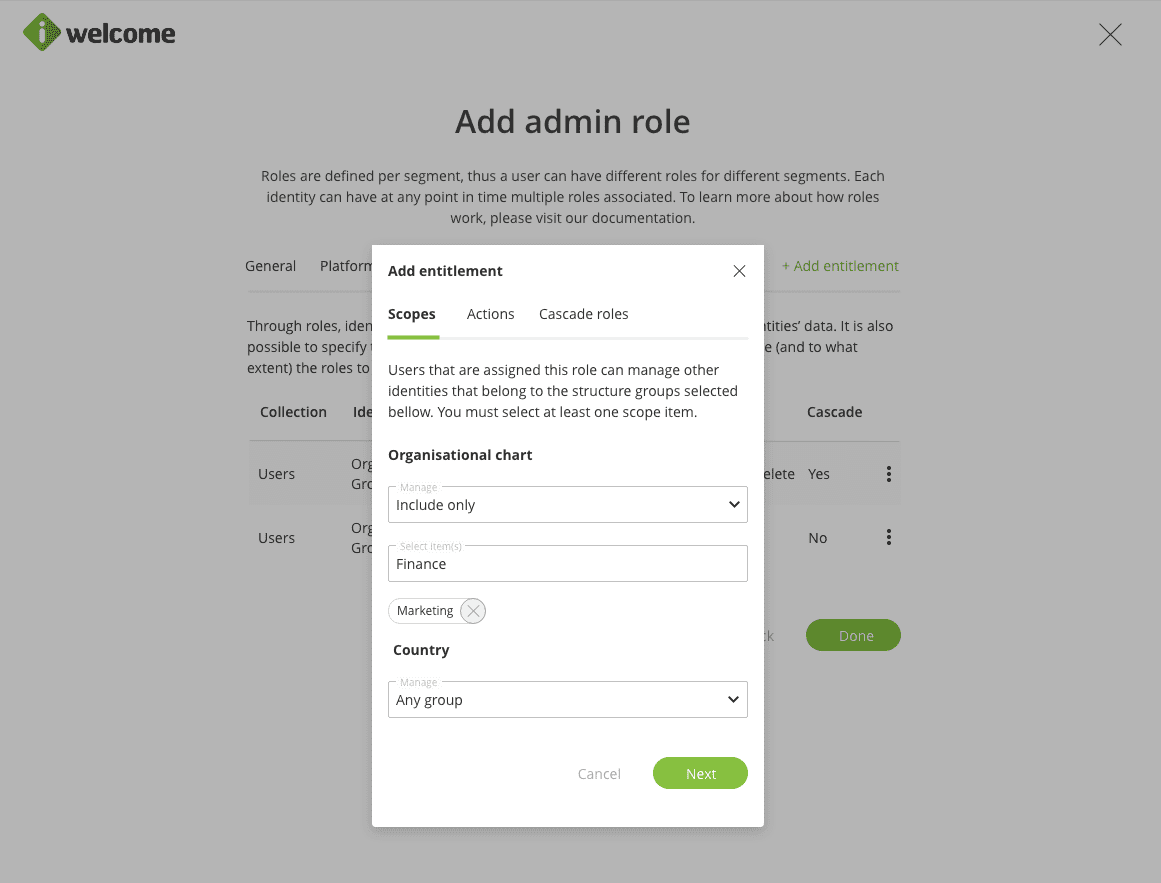
The first step in adding an entitlement is to define the scope. Scope restrictions are applied through segments structures & related groups. Applying a structure related restriction requires the admin user to select the structure(s), a qualifier and (potentially) one or more groups belonging to that structure.
The system implements five qualifiers:
- Any group - this means that all users will be included in the scope, regardless of the specific group associated with the structure they are in;
- Ignore - none of the users from the structure will be included in the scope;
- Common (and nested) groups - selecting this option will restrict the scope to users that share the same group as the user having the role associated;
- Include onlys - this will restrict the scope to the users belonging to the exact groups that are selected;
- Include any group, but - the scope will include all the groups from the selected structure except the groups that are selected.
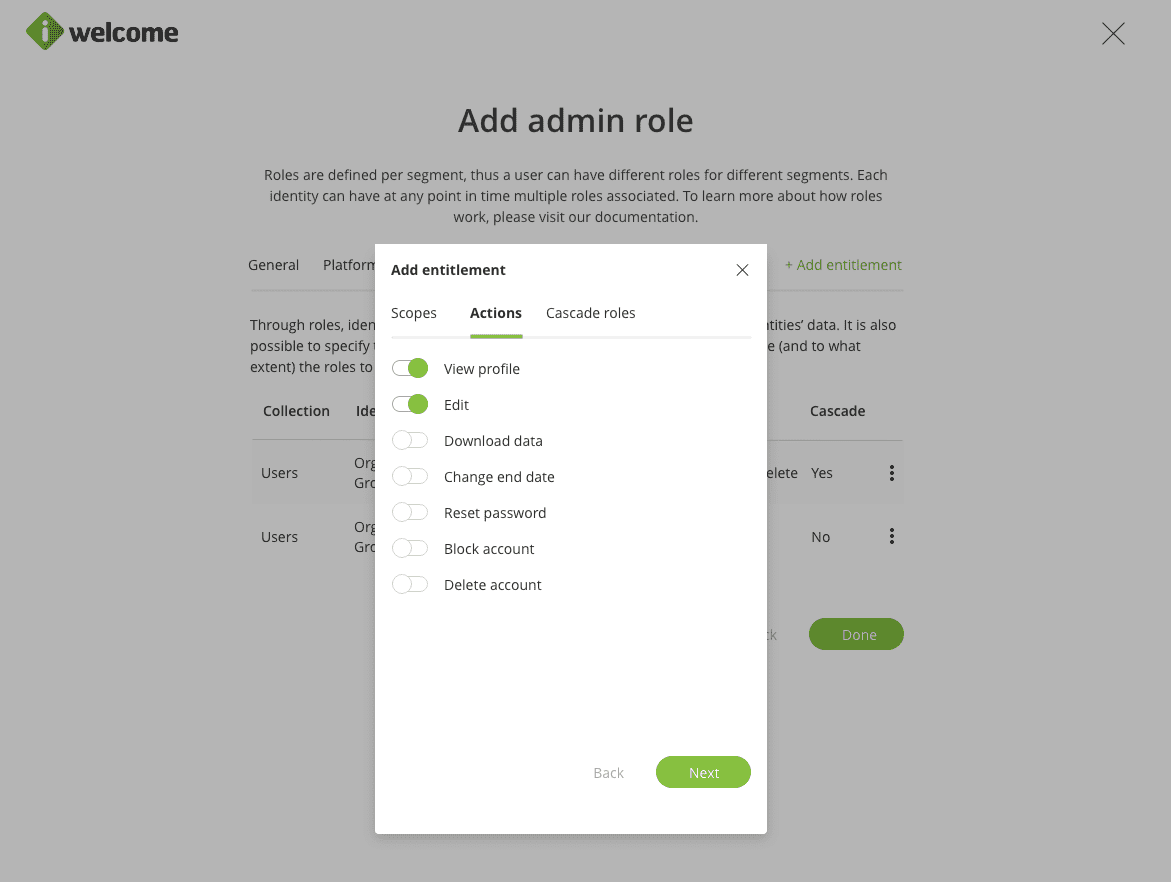
The next step is to select the action that the role can perform on the selected users.
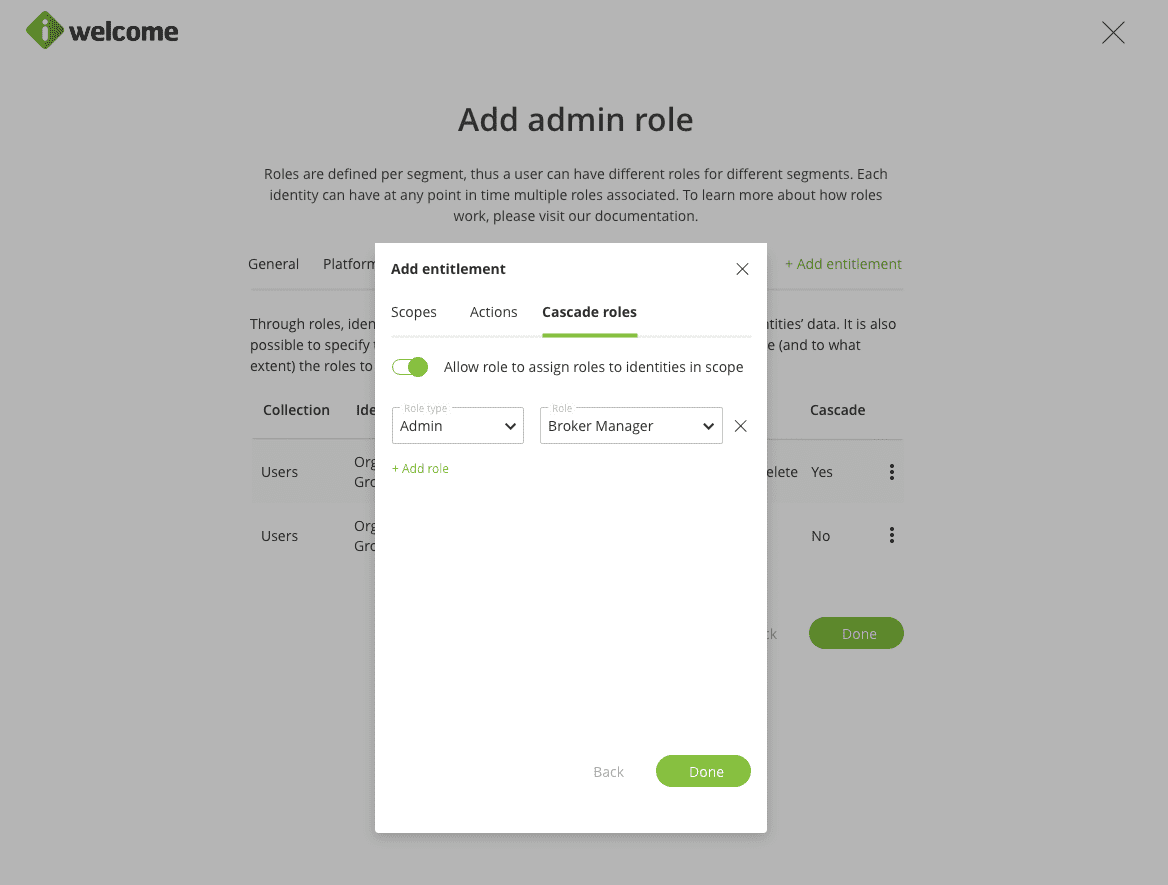
Finally, the last step is to select what roles a user with the current role can assign to the users in scope. As the roles that can be cascaded have to be already defined, it is advisable to define them before the role that will have the cascade capabilities.
Personal role
This role controls what personal data a user may access and what actions he/she can perform on the self service page.
The personal role governs whether a user can request access to roles defined within the platform, download their personal or event-related data, or delete their account.
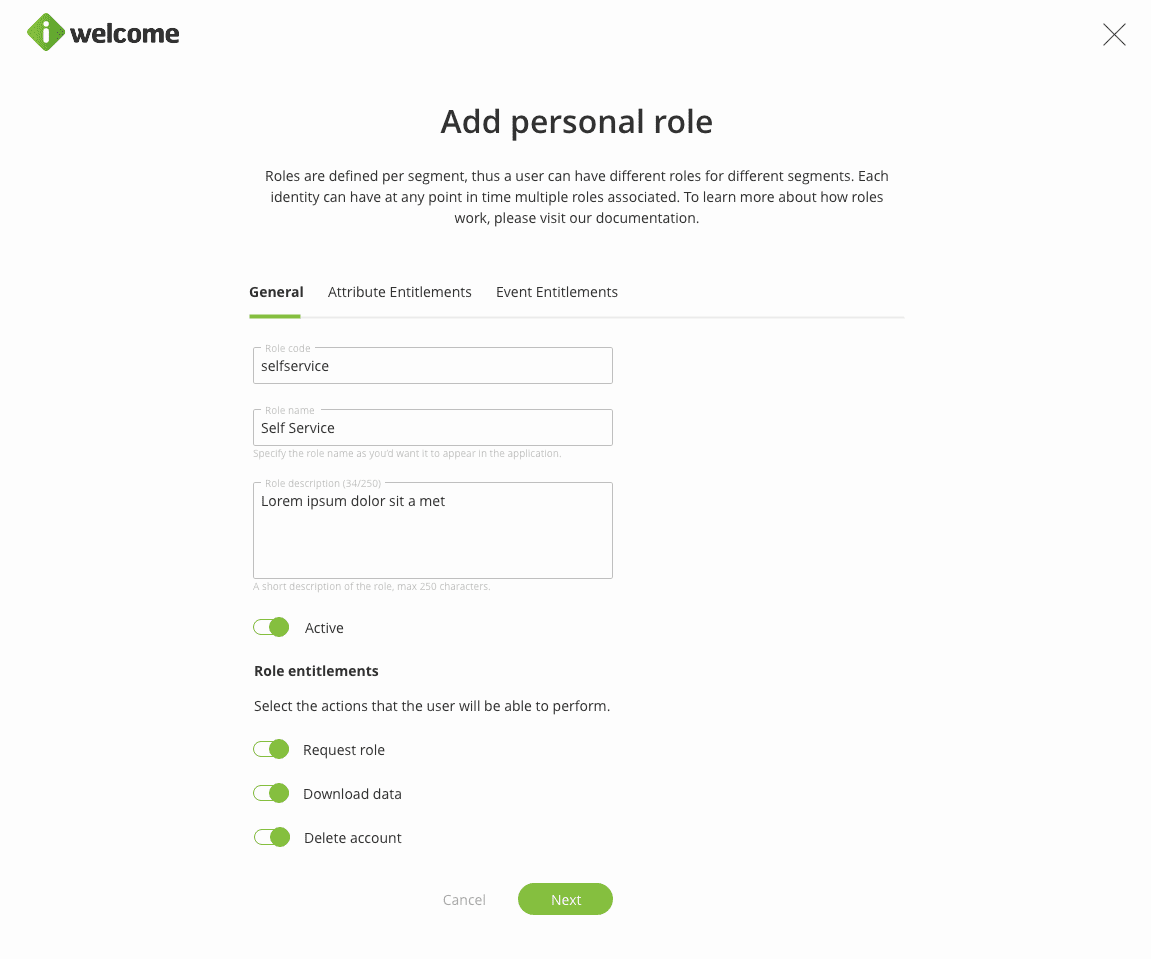
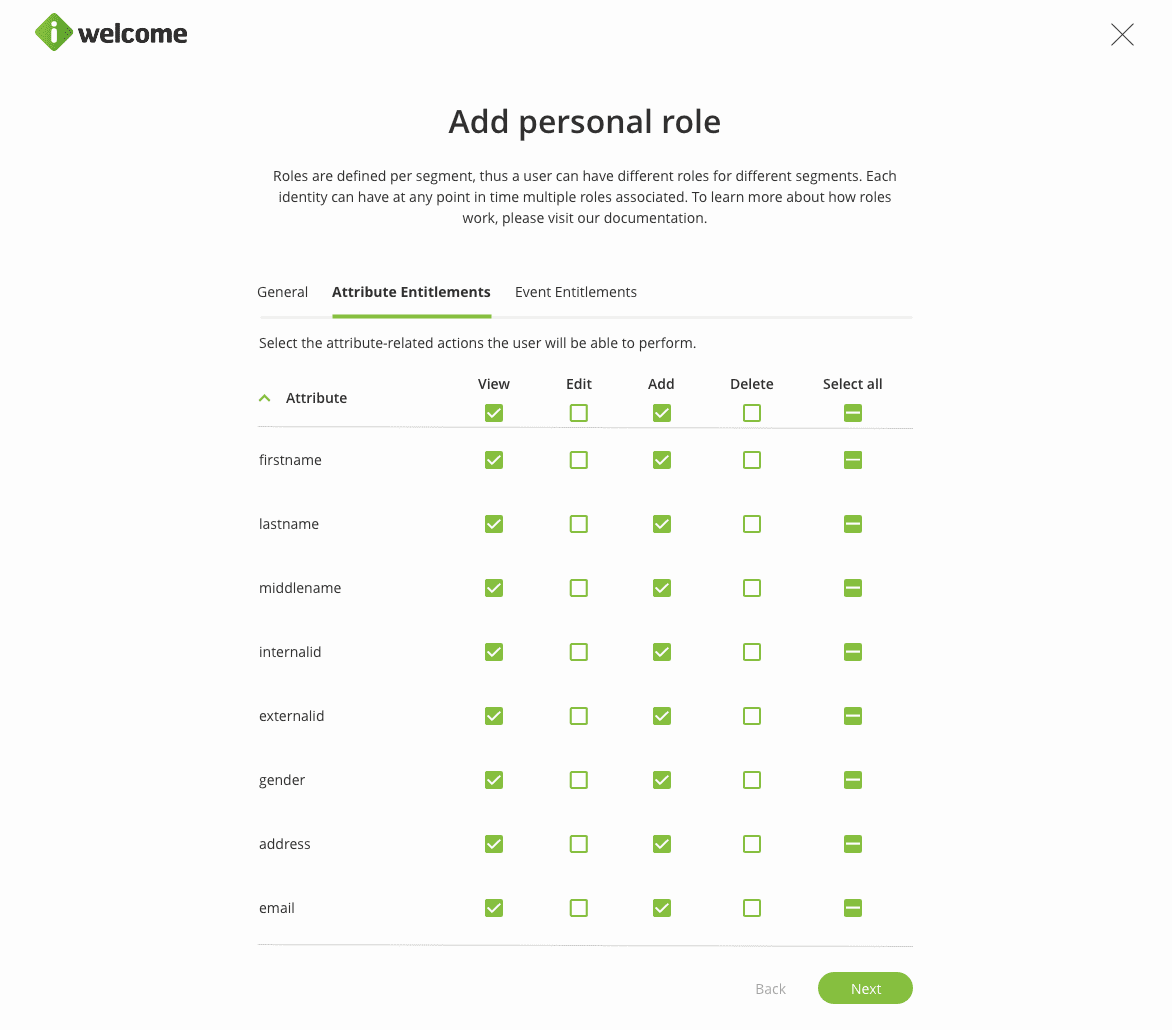
Additionally, through the personal role, a user can be allowed to view, edit, add or delete his attribute-related information:
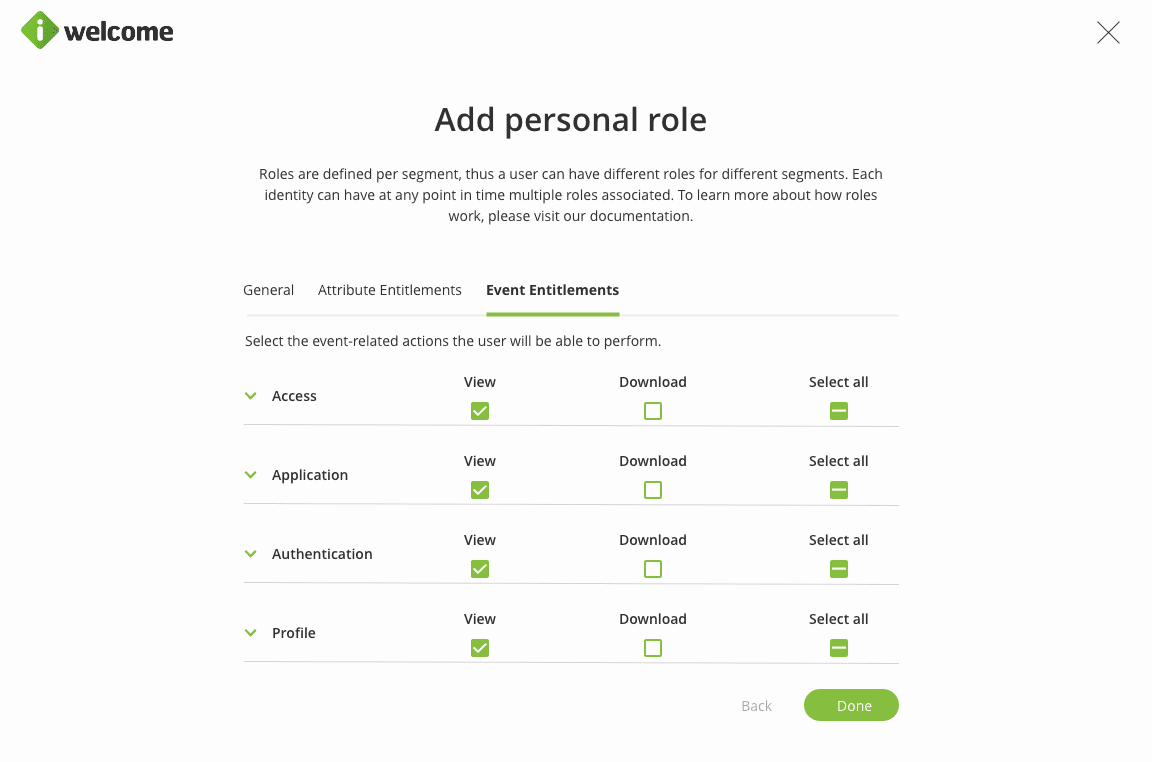
As well as to view or download event-related information:
Regardless of the role type, when adding a role, the organisation will have to assign it a code, name, description and select the segment of identities that the role can be assigned to.
Accessing roles
A user is only able to access the Roles configuration menu item within the platform and to create new roles if that user has at least one Admin role that grants him that permission.
Furthermore, considering that the user was granted access to the Role menu item, he is only able to manage the roles created by him and the ones that he can cascade (assign), but not the roles that he has himself.
Editing a role
A role's code cannot be edited. Apart from them, the rest of the fields (including the data specific to each role type as described below) can be edited at any given point in time and the changes will apply right away.
Deactivating a role
Deactivating a role will not affect current users and their relations with it, but will make the role unavailable for future use (e.g. association to other identities). In case the role was used in a rule, it will not be applied anymore.
Deleting a role
Deleting a role is irreversible and will imply removing it from users' profile. Note that removing roles from users' profile will not happen instantaneously, but through a system job that runs periodically.
Rules
You can set up rules for the system so that they will automatically modify attribute values, group memberships or assigned roles for all the identities that fall under the conditions that you set.
Data value conditioned rules
When adding a rule, the first step will be to assign a code, name & description to it. The rule created below assigns changes the attribute value for the job type for all the identities that match the attribute-related criteria.
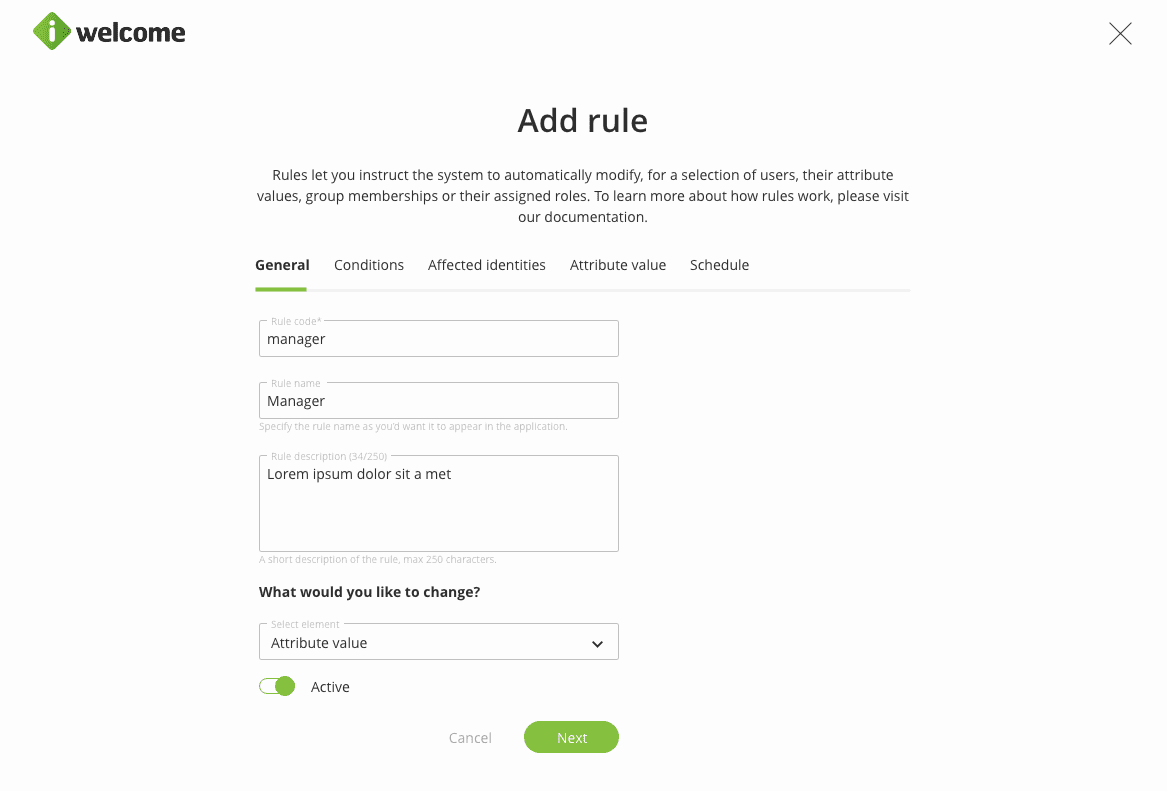
To restrict the scope of the rule, the organisation might use structure or attribute-based conditions. A rule might contain several sets of conditions.
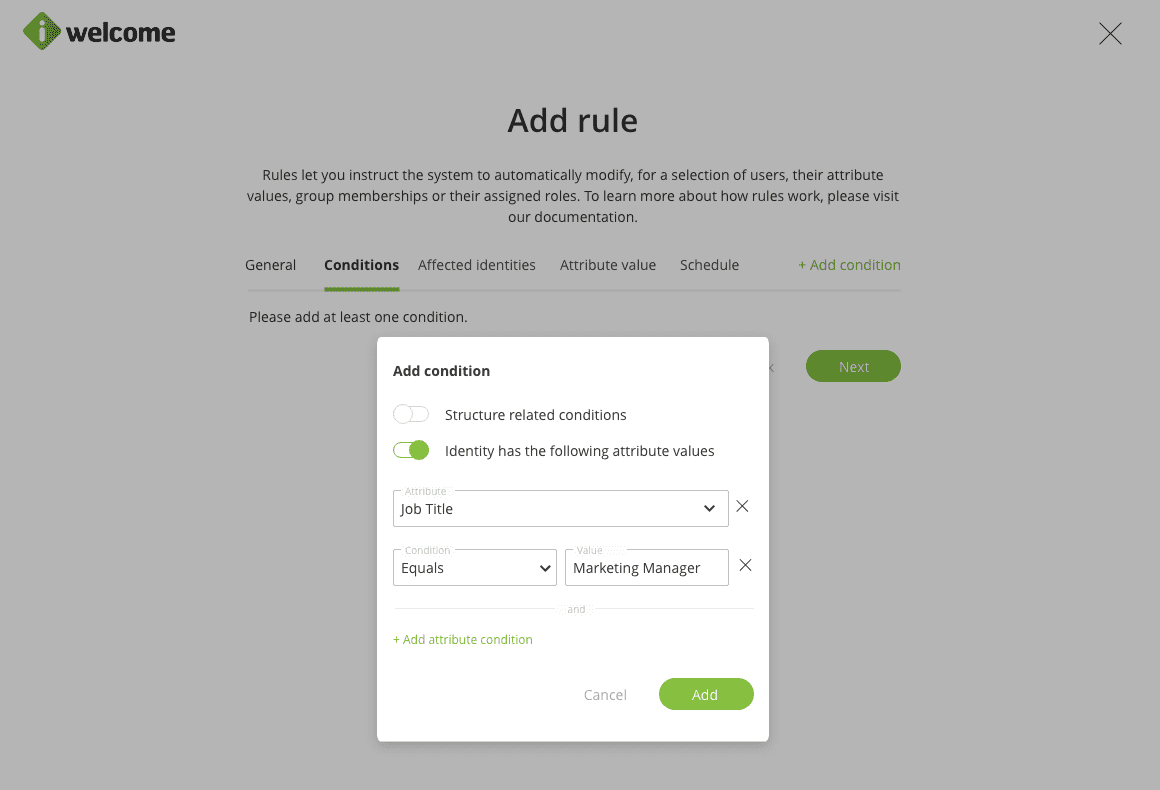
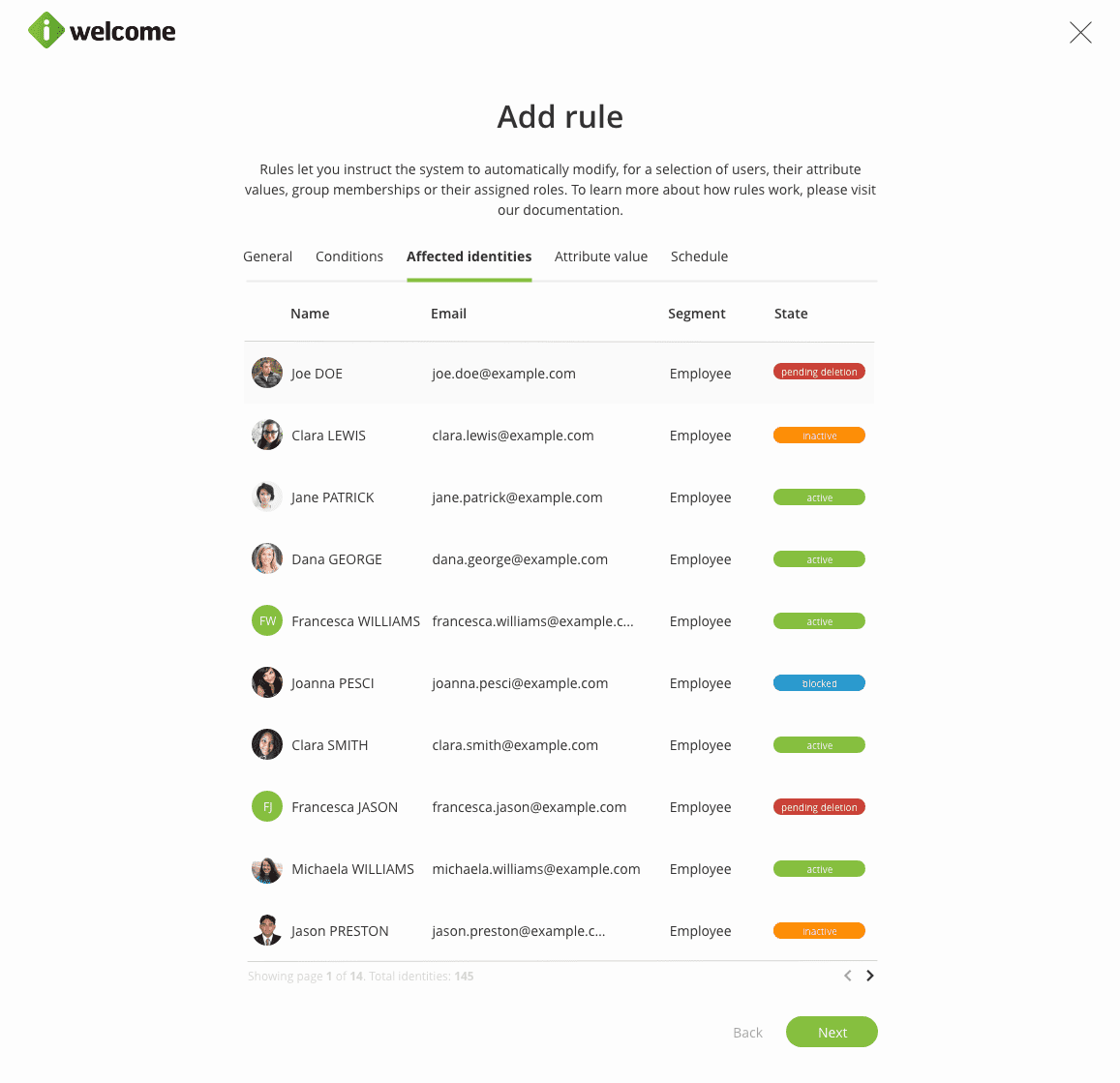
Based on the selected conditions, the tab Affected identities will display the current list of identities that will be affected by the rule. Note that the list might change depending on the changes in users' attributes or their associated groups.
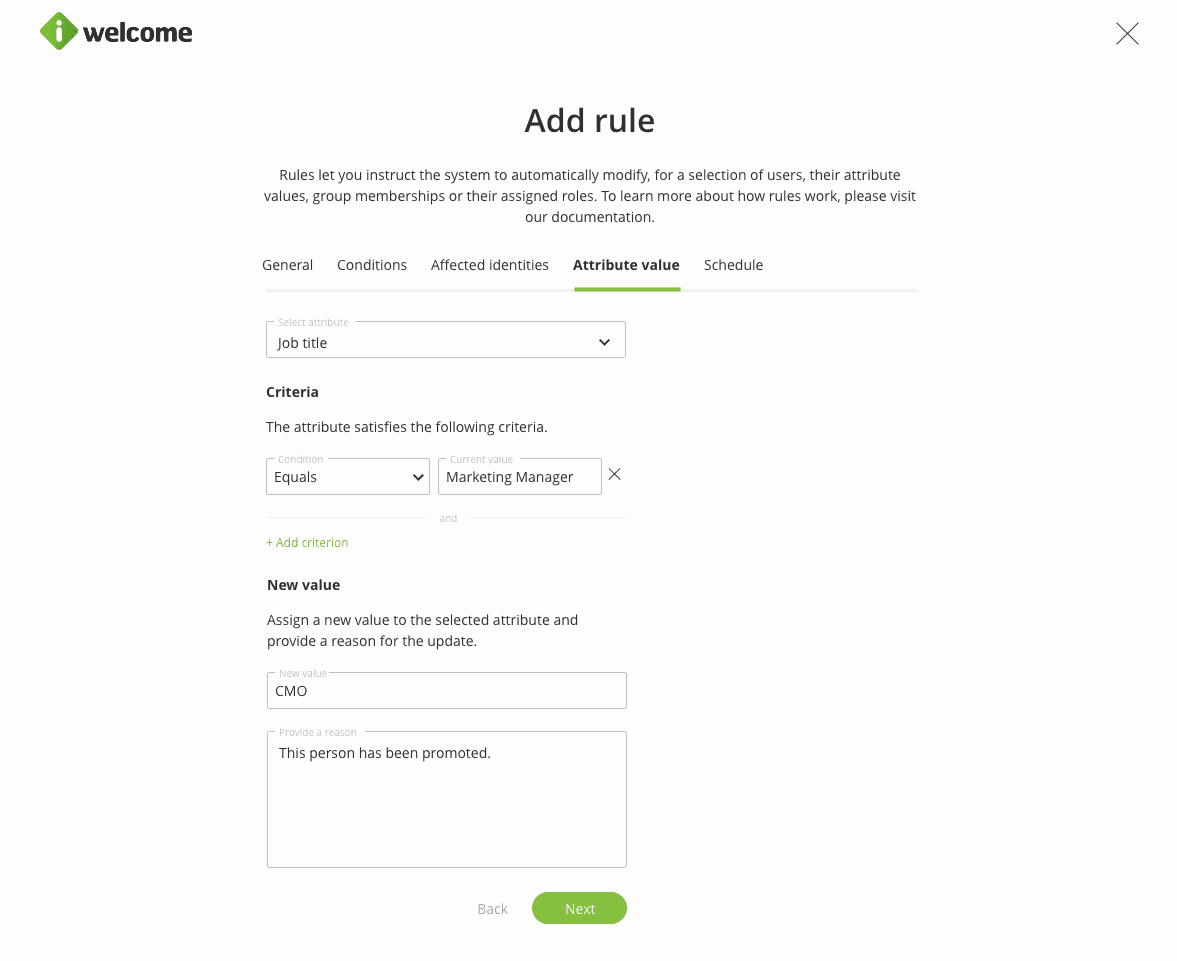
Going forward, the admin user will have to specify the new attribute value that will be assigned to the users in scope.
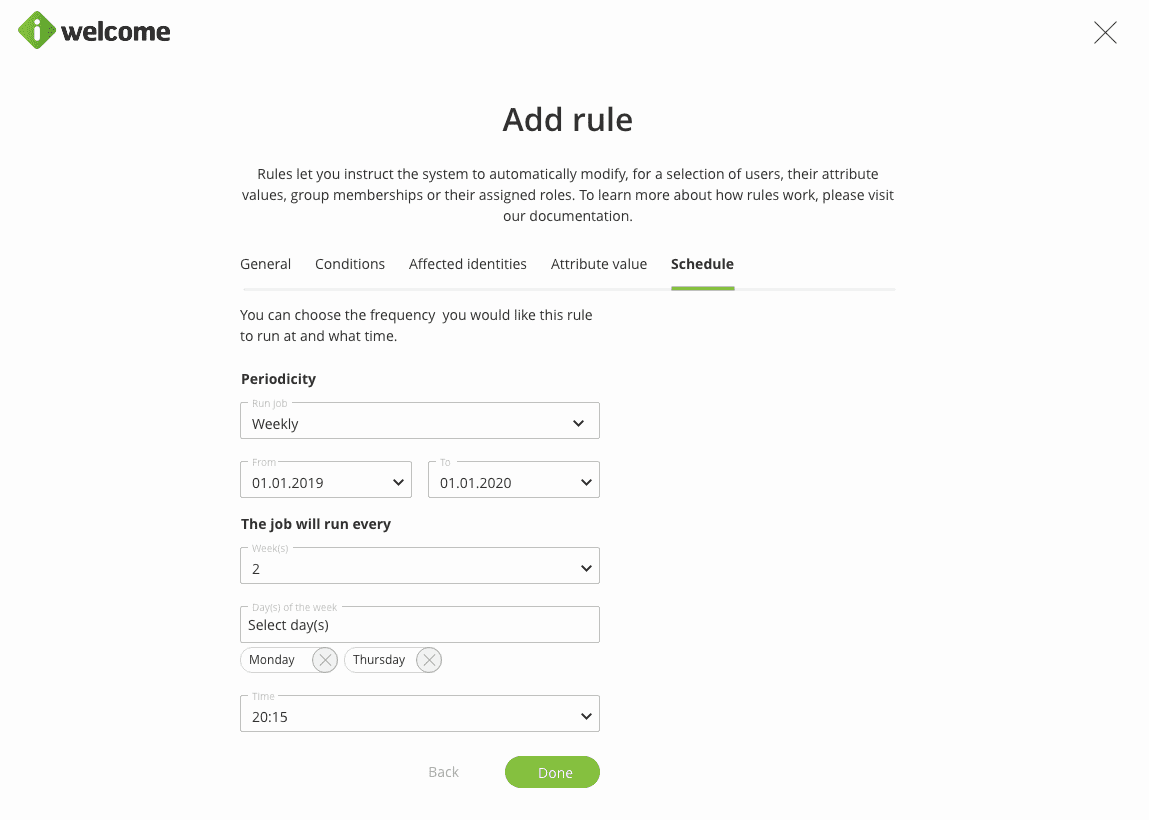
The last step of the data value conditioned rule is to establish the periodicity of when the rule should run, as part of the Jobs section.
Accessing rules
A user is only able to access the Rules configuration menu item within the platform if that user has at least one Admin role that grants him that permission. Users that have this permission are allowed to create new rules and manage all the existing ones.